Name
cx:plantuml — Draws diagrams with PlantUML.
Synopsis
This step constructs diagrams with PlantUML.
| Input port | Primary | Sequence | Content types |
|---|---|---|---|
| source | ✔ | text |
| Output port | Primary | Sequence | Content types |
|---|---|---|---|
| result | ✔ |
| Option name | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| format | xs:string? | 'png' |
| parameters | map(xs:QName, item()*)? | () |
<p:import href="https://xmlcalabash.com/ext/library/diagramming.xpl"/>Declaration
1 |<p:declare-step xmlns:cx="http://xmlcalabash.com/ns/extensions"
| xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc"
| type="cx:plantuml">
| <p:input port="source" content-types="text"/>
5 | <p:output port="result"/>
| <p:option name="format" as="xs:string?" select="'png'"/>
| <p:option name="parameters" as="map(xs:QName, item()*)?"/>
|</p:declare-step>Description
The cx:plantuml step constructs diagrams with
PlantUML.
PlantUML supports a wide variety of diagrams, not just UML diagrams.
The mapping from output formats to content types isn’t 1:1, so you must specify the format explicitly. Available formats (at the time of writing) are:
| Format | Content type |
|---|---|
atxt | text/plain |
base64 | text/plain;charset=x-user-defined |
braille-png | image/png |
debug | text/plain |
eps | application/postscript |
eps-text | application/postscript |
graphml | application/graphml+xml |
html | text/html |
html5 | text/html |
latex | application/x-latex |
latex-no-preamble | application/x-latex |
pdf | application/pdf |
png | image/png |
preproc | text/plain |
raw | image/raw |
scxml | application/scxml+xml |
svg | image/svg+xml |
utxt | text/plain;charset=UTF-8 |
vdx | application/vnd.visio.xml |
xmi-argo | application/vnd.xmi+xml |
xmi-script | application/vnd.xmi+xml |
xmi-standard | application/vnd.xmi+xml |
xmi-star | application/vnd.xmi+xml |
XML Calabash uses 1.2026.1 of the PlantUML library.
Examples
The PlantUML user guide includes many examples. The UML source in Example 1, “UML source” renders to the image show in Figure 1, “UML diagram”.
@startuml
skinparam backgroundColor #FFFFF8
class BaseClass
namespace net.dummy #DDDDDD {
.BaseClass <|-- Person
Meeting o-- Person
.BaseClass <|- Meeting
}
namespace net.foo {
net.dummy.Person <|- Person
.BaseClass <|-- Person
net.dummy.Meeting o-- Person
}
BaseClass <|-- net.unused.Person
@enduml
Another example shows how JSON can be rendered. The object in Example 2, “JSON source” renders to the image show in Figure 2, “JSON diagram”. (Note the use of pragmas for highlighting.)
@startjson
skinparam backgroundColor #FFFFF8
#highlight "lastName"
#highlight "address" / "city"
#highlight "phoneNumbers" / "0" / "number"
{
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Smith",
"isAlive": true,
"age": 28,
"address": {
"streetAddress": "21 2nd Street",
"city": "New York",
"state": "NY",
"postalCode": "10021-3100"
},
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "home",
"number": "212 555-1234"
},
{
"type": "office",
"number": "646 555-4567"
}
],
"children": [],
"spouse": null
}
@endjson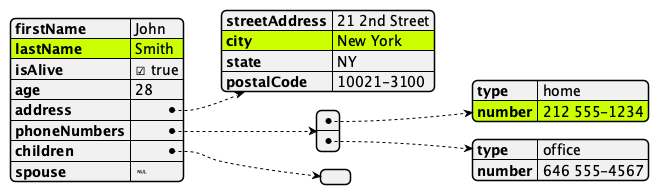
A final example (but by no means an exhaustive list of all of the possible examples) shows the PlantUML EBNF for PlantUML. The EBNF in Example 3, “JSON source” renders to the image show in Figure 3, “EBNF diagram”. (Note the use of pragmas for highlighting.)
@startebnf
skinparam backgroundColor #FFFFF8
grammar = { rule };
rule = lhs , "=" (* definition *) , rhs , ";" (* termination *);
lhs = identifier ;
rhs = identifier
| terminal
| "[" , rhs (* optional *) , "]"
| "{" , rhs (* repetition *), "}"
| "(" , rhs (* grouping *) , ")"
| "(*" , string (* comment *) , "*)"
| "?" , rhs (* special sequence, aka notation *) , "?"
| rhs , "|" (* alternation *) , rhs
| rhs , "," (* concatenation *), rhs ;
identifier = letter , { letter | digit | "_" } ;
terminal = "'" , character , { character } , "'"
| '"' , character , { character } , '"' ;
character = letter | digit | symbol | "_" ;
symbol = "[" | "]" | "{" | "}" | "(" | ")" | "<" | ">"
| "'" | '"' | "=" | "|" | "." | "," | ";" ;
digit = ? 0-9 ? ;
letter = ? A-Z or a-z ? ;
@endebnf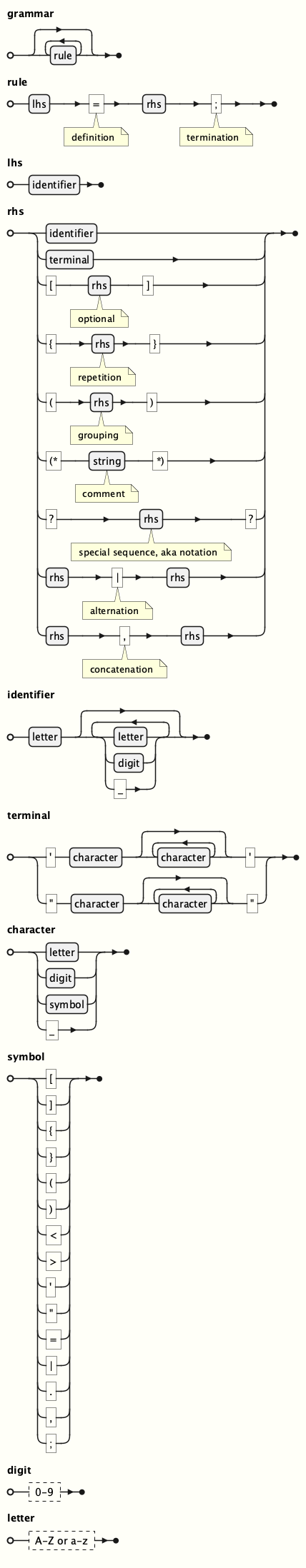
Dependencies
This step is included in the XML Calabash application. If you are getting XML Calabash from Maven, you will also need to include the additional dependency:
net.sourceforge.plantuml:plantuml:1.2026.1